Have you already wondered why some sites rank for competitive keywords with low domain authority?
The answer: They use SEO entities to boost their content relevance.
Read this article to learn about entity optimization, a simple strategy that could help you outrank your competitors!
What is an SEO Entity, and Why is it so Important?
Entity SEO is an advanced approach to SEO concerning both on-page and off-page optimization. Following the semantic evolution of search engines from Lexical to Semantic, Entity SEO considers not the keywords but the entities (topics or subtopics) that define the page’s topic.
The article “Introducing the Knowledge Graph: things, not strings,” published in the official Google Blog in 2012, is the watershed marking the birth of Entity SEO. Even though the diffusion of the concept is already a couple of years old, its adoption in the daily practice of SEOs is still uncommon.
The “strings” in the title are the sequences of characters that constitute keywords.
Simplifying, we can say that “things” is more or less a synonym for entities.
In general, entities are objects or concepts that can be uniquely identified, often people, places, brands, and “things,” in fact.
Knowledge Graphs: A Visual Database of Entities and Relations
A Knowledge Graph is a visual representation of a Knowledge Base such as Wikipedia or IMDb.com. It is made of Entities and their Relationships, which constitutes the database in which Google stores its factual knowledge about the world. That “knowledge” is defined by Google precisely as the system of relationships between entities.
By showing search engines a deep knowledge of the main topic we deal with, we will gain what is called Topical Authority in their eyes.
It is, therefore, necessary to produce content that explicitly shows the dense semantic network constituted by all the entities that define a topic and that tend to co-occur with some frequency in the pages to which Google assigns first positions in the SERP.
How Having a Knowledge Graph Can Boost Your Site
“A knowledge graph describes objects of interest and connections between them.” (Natasha Noy et al. Industry-Scale Knowledge Graphs: Lessons and Challenges).
Specifically, this paper states that “a knowledge graph describes objects of interest and connections between them. […] Knowledge graphs provide a shared substrate of knowledge within an organization, allowing different products and applications to use similar vocabulary and to reuse definitions and descriptions that others create.”
Structurally speaking, a Knowledge Graph is s Knowledge base made of Nodes and Edges (sometimes called Arches).
Nodes are entities, and Edges are the relationships between those entities.
Each Entity is stored as a “triple” consisting of Subject-predicate-object.
We can also look at it another way: Entity-relation-entity.
In such a way, we emphasize the interconnection between entities and how each can be part of the description of other entities (as its attribute or as an object of a subject), thus forming the dense semantic network we were talking about.
Many SEOs just ignore that it is possible to create a Knowledge Graph of one’s site using the schema.org vocabulary to structure our content/data in a way that is immediately understandable to search engines or other “intelligent agents,” e.g., a conversation agent may be created on the top of a site-level Knowledge Graph to answer users’ questions.
If you want to go further with Knowledge Bases and Graphs theory, read this slide deck by Massimiliano Geraci:

What Are Structured Data, and What Are They Used For?
Structured data are this metadata added to HTML. They can be expressed using different vocabularies (Ontologies, to be more precise) and markup languages, schema.org and JSON-LD being the most used.
As an author or digital marketer, keep in mind that you have two different audiences, one is human the other is search engines. Implementing unique structured Data is the best way to make it explicit to Search Algorithms:
- The structure of a Webpage, i.e., the discrete units of content on it: a video, an accordion with FAQs, a list/feed of products, your contacts, a map showing you LocalBusiness position, etc.;
- the relationships among these various discrete units of content on the page as well as among the site as a whole;
- The topics covered, i.e., the entities that contribute to defining it.
Semantic Publishing
Semantic Publishing is publishing a page on the Internet by adding a semantic layer (i.e., semantic enrichment) in the form of structured data that describes the page itself.
Semantic Publishing helps search engines, voice assistants, or other intelligent agents understand the page’s meaning, context, and structure, making information retrieval and data integration more efficient.
Semantic Publishing relies on adopting structured data to describe the WebPage as an entity made of connected content blocks, partOf a Website, written by an Author, reviewedBy a Physician if it is a MedicalWebPage (pushing your EAT – Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness – is another important advantage of implementing advanced structured data), published by an Organization, and so on.
When following an entity-based SEO approach, the key step, however, is to make explicit within the Structured Data the main entities present on the page by relating them to trustable sources in a way that there is no ambiguity (this process is called Entity-linking an we are going to discuss it in a moment).
Remind that the structured data, expressed in the JSON-LD language, are present in the page’s header and read by Google before anything else, providing it with the first basic clues to understanding and classifying the page’s content accurately enough.
How to Find SEO Entities?
There are two strategies for entity detection. The first is to observe those explicitly present in Google products.
For example, these entities in the “bubbles” that appear in image search or above the image carousels in General Search.
Also, entities are the topics that Google invites us to click on to define our interests to customize the Discover feed.
Another way to identify the entities in the content that Google ranks for a query is to use Natural Language Processing (NLP) models trained to recognize these entities by processing a text.
By analyzing the entities shared by pages in the top 10 search results, we can know what topics and subtopics (and their relative relevance) Goole aspects to find within our content.
As in the case of traditional keyword research, to identify entities The starting point is competition analysis. Which entities do they include in their content? Which attributes? There are niche-dependant patterns that you will start to recognize over time.
It’s only being really exhaustive, covering all the entities related to your topics that you can to outrank your competitors.
You can use Wikipedia, Reddit, or relevant forums to your target niche, product reviews on e-commerce or independent sites, academic papers, hard-to-find whitepapers, slides published on Slideshare, the video descriptions on Youtube, the feed in a Facebook group, or comments on an Instagram post, to name a few places worth keeping an eye on. An NLP model can analyze even these types of pages, or you can copy or scrape the text you need and let The Entities Swiss Knife make the magic for you.
The less “obvious” entities emerging from this analysis are useful not only in defining our topic and gaining Topical Authority.
Providing information that is not obvious and otherwise more difficult for our users to find is the best way to show Google how you produce “useful content” with a real informative value and not just another “commodity content” which is yet another copy of what is on the Internet.
How to Inject SEO Entities Into Your Site? Entity-linking and Structured Data
Entity Linking is the process of identifying entities in a document and relating these entities to their unique identifiers in a Knowledge Base.
Wikification occurs when entities in the document are mapped to entities in Wikimedia Foundation resources, namely Wikipedia and Wikidata.
The Entity-based SEO approach at the core of the optimization method we are going to present to you relies on Entity-linking.
The schema vocabulary properties used for Semantic Publishing -that bridge between Structured Data and Entities- are the about, mentions, sameAs, and knowsAbout, and you will see them in action in the second part of this article.
These properties are as powerful as they need to be more utilized by SEOs partly because of the most diffused SEO plugins that automate Structured Data creation, such as Yoast and Rankmath. Those plugins do not allow immediate user modification of structured data (filters and hooks would have to be used to do this), so very slight customization is allowed.
It has now been demonstrated many times that the presence of Structured Data is a ranking factor, and not only a traffic source related to Rich Results, the particular spots in Google’s SERP that your pages are legible to win only if they have the right structured data.
The main limitation, however, is that by relying on plugins such as those mentioned, every site will have Structured Data virtually identical to every other. Thus they cannot be a differentiating factor to be rewarded by Search Engines.
4 Strategies to Leverage Entity SEO to Make Your Site a Topical Authority Website
1. Build Your Website Structure Using SEO Entities
Building a proper site structure is an important step if you want Google to understand your content well. There is nothing better than structuring your website using the power of Semantic Publishing and presenting it as a Knowledge Graph connected to trustable public Knowledge bases.
Let’s use this as an example; when you organize your photos… you make it easy for you or anyone that will open your photo folder to retrieve any photos, right? You will create folders by year, by event, etc….…
We’ll do the same with our website. When Google starts to crawl your website, it needs to understand which topics you are covering. To make it easy for Google to understand your content, you must organize it by topics.
Let’s look at my website (Israel is writing here) if you pay attention to the top menu, you will see the main topics I’m covering:
Each of these categories is associated with an entity.
Generally speaking, entities have an entry on some public Knowledge Base, but remember that it’s not always the case.
As you know at this point, the strategy we want to share with you is based on Entity-linking -particularly Wikification- and so we will refer only to entities present on Wikipedia or Wikidata, which are a big part of what Google uses as a reference for its Knowledge Graph.
If you click on one of the entities above, you will be redirected to their Wikipedia pages.
Now, if you look at the schema, you will see that the entity name is injected as the value of the about schema property of my category page. More precisely, it is part of a Thing schema type nested in the WebPage schema type. The entity is also linked (wikified) to the Wikipedia and Wikidata pages using their URLs as the value of the sameAs property.
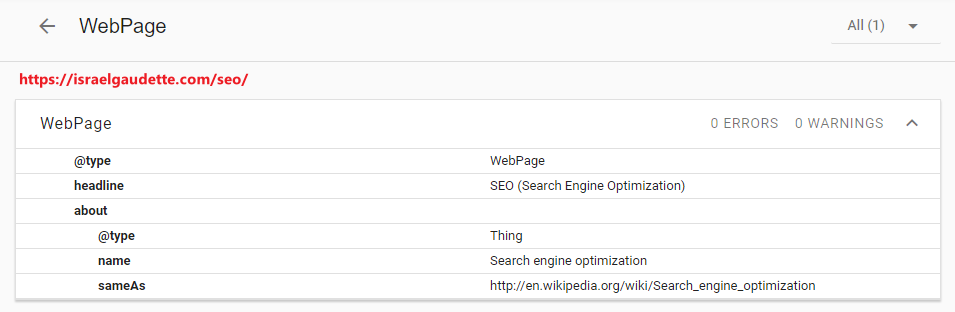
Now, it is clear to Google that my silo “/SEO/” is about “Search Engine Optimization.”
Maybe for you, it’s clear that SEO means “Search Engine Optimization,” but if you look deeper, you will see that SEO has multiple entities associated with it… and Google may be confused.
Using the correct entity in your schema will avoid any confusion!
Okay, so now that our website is organized for a specific topic, it’s time to organize our content.
To achieve this, we’ll use The Entities Swiss Knife. I suggest you create a Google Sheet to help you categorize your content by topics and sub-topics, and then afterward, assign them to your different website silos (topics).
A Silo head has its main Topics/Entities declared as about properties and the sub-topics as its mentions. These sub-topics are fully developed in supporting articles, each one focused on (about property) a single sub-topic “mentioned” in the Silo head (or a Pillar page in a content HUB structure).
You can see an example here.
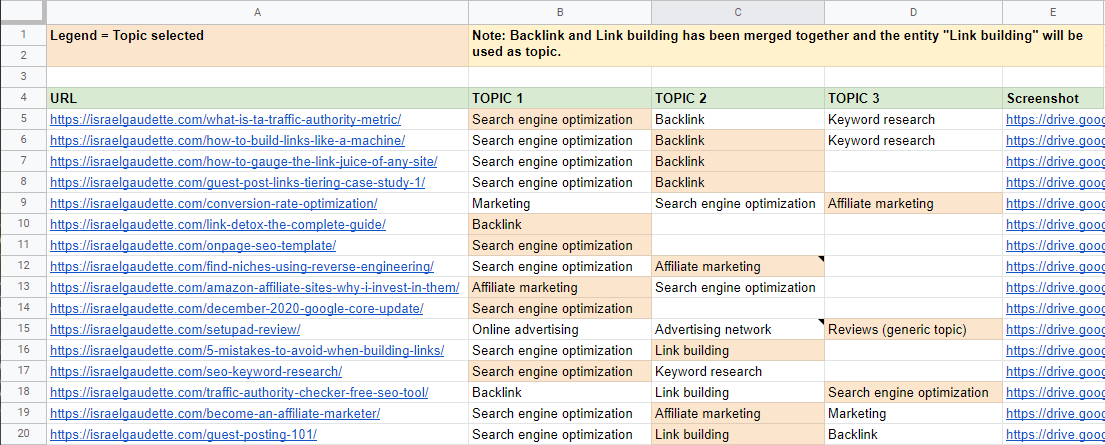
So basically, I noted the 3 top topics for each article and tried to organize my website sub-topics, or related topics, based on these 3 main ones. I used the “Topics” data from The Entities’ Swiss Knive for building this list of topics.
Once I was done, I added colors to the assigned topic for all my articles. I ended with 4 categories, including one generic (Reviews); all the others are based on an entity.
Important: Be careful because sometimes the topics suggested haven’t a Wikipedia/Wikidata entry! You must check and ensure your topic matches a dedicated page on one or both. Otherwise, find the most relevant linkable entity (i.e., present on a trustable public Knowledge Base) closely related to your main topics.
As we told at the beginning of the article, you can also use the Internet Movies database, IMDb.com, as a linking source if your main topics are related to the Arts & Entertainment or Crunchbase.com if they are business related.
The next step is to create one post category for each topic and assign your content to it.
Create a dedicated page for all your post categories (Always index your category pages!), and inject the entity (i.e., Affiliate marketing) in your schema as an about property.
You can generate the schema markup with The Entities’ Swiss Knife. Select your entities in the about and mentions field, and click to download the JSON file.
You must use our WP plugin to inject your entities into the correct schema, identified by its @id.
Each schema type present on your site (can) have a unique identifier, generally made of the page URL and a static or sometimes dynamic suffice appended to it. JSON-LD allows you to interlink different schemas, or nest them, referencing their identifiers with the @id property, thus creating the dese semantic network and telling a detailed story about your site immediately intelligible to the Search Engines.
You can download The Entities Swiss Knife plugin from the homepage by clicking the button on the sidebar.
2. Topics Gapping: Optimize Your Content Using The RIGHT Entities
Topics gapping (also called Entity GAP Analysis) is the concept of looking at the top competitors and finding the most important shared entities that YOU SHOULD HAVE in your content.
Of course, you can use a tool like Surfer SEO to help you find the important keywords to inject into your content, to make it the most relevant as possible… But this may not be enough to outrank the competition!
Most (if not all) of the content optimization tools extract not only entities. They also suggest recurring n-grams (strings of -usually- 2 to 4 words). Besides, not all the suggested entities have a URL so they can be useless for our strategy based on Entity-linking.
The tool I’ve built in collaboration with Max has two special features called 1) “SERP analysis” and 2) “Entities GAP analysis”. These features will let you discover the most important “Things” entities covered by top-ranked content (1) and find the gap (2) to fill it. You can do this in just a few easy steps:
SERP Analysis:
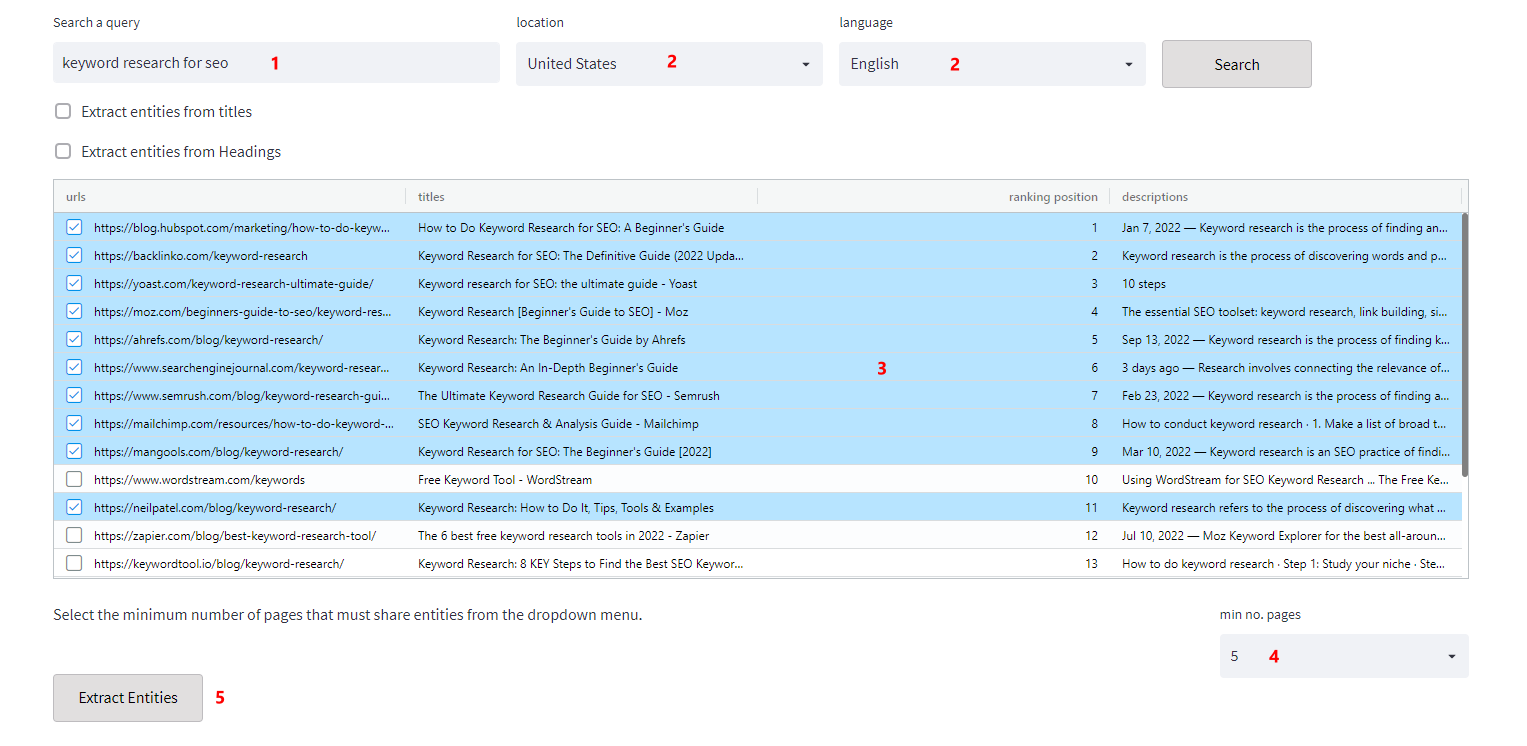
- Write your query;
- Select your country and language;
- Select your competitors;
- Select some results, and from the dropdown menu select the minimum number of pages that need to share the entities you are interested in. As an overview, select 10 results and 5 to discover the prominent entities associated with a Search query. Choose 1 if you want to see ALL the entities extracted from your competitors’ pages. You can also decide to see which are the entities shown on the SERP limiting the analysis to the Tag_titles and meta descriptions.
- Click on “Extract Entities”
Entities GAP Analysis:
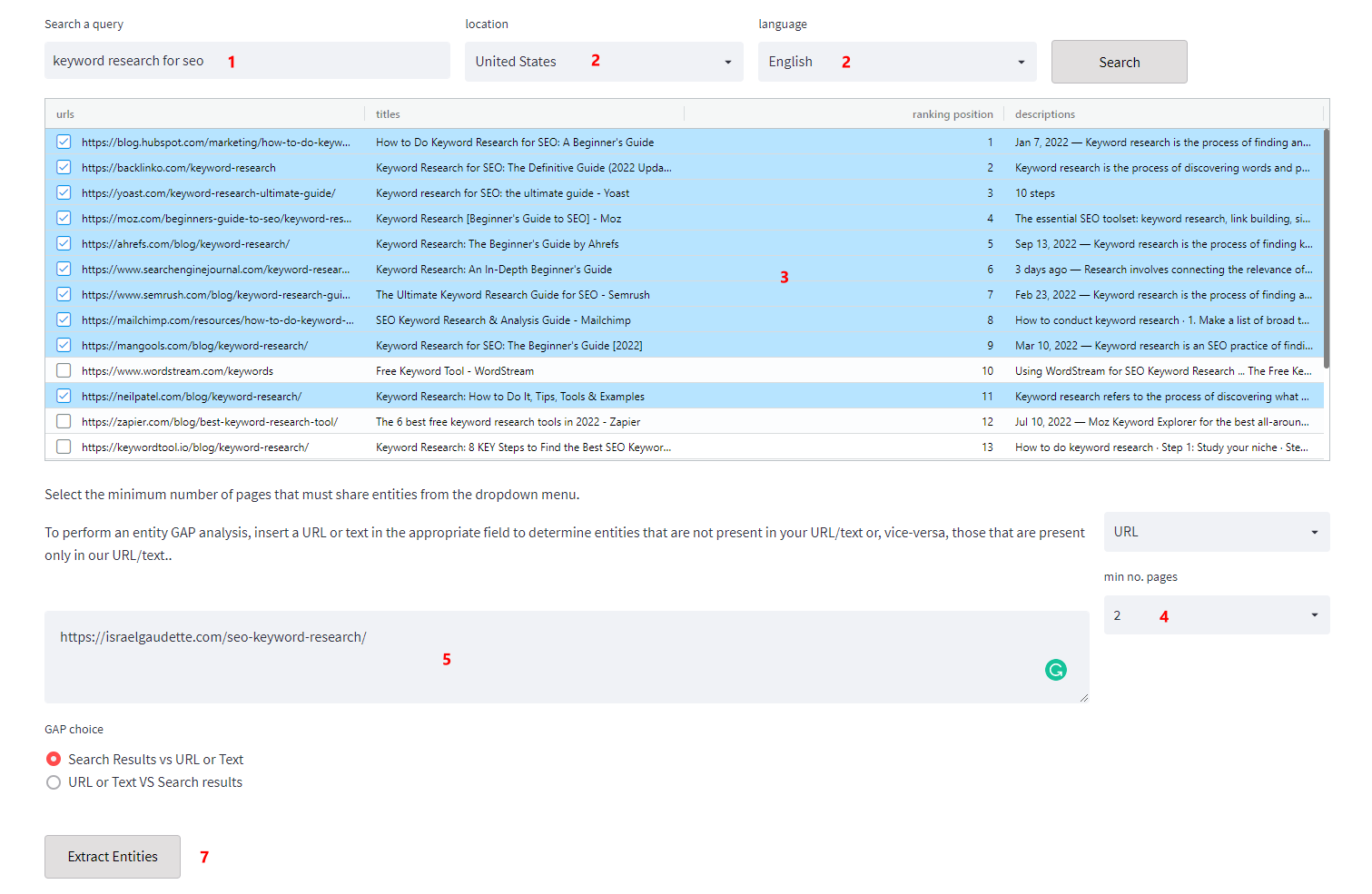
If you have already published your article, or have written it, you can proceed with the GAP analysis. Follow the 1-4 steps and then
- Add your URL or Text to compare with (don’t check it from the Search results if it’s there);
- Choose the minimum number of pages that need to share the entities you are interested in (You can leave this on default);
- Click on “Extract Entities”.
Once executed, a table will appear. I recommend just skipping this and scrolling to the bottom of the page, and downloading the report in Excel format.
The current app relies upon the Streamlit python library for a fast and basic User Interface design (this will change soon), and this has serious limitations on how we can present data. That is why we recommend analyzing your data in Excel as the presentation is more readable.
The Excel report will look like this:
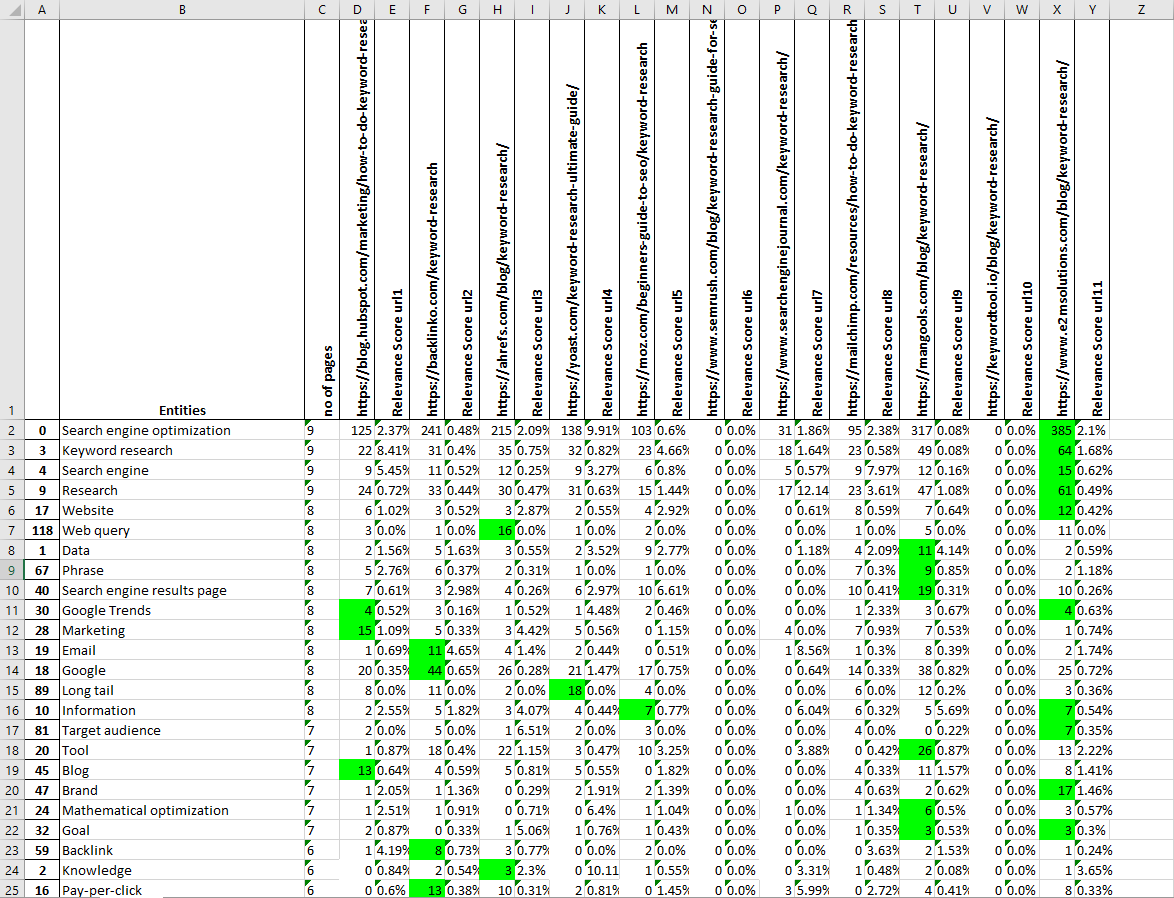
In the top row, you will see the competitors’ URLs, followed by the list of entities ranked by their “importance” (called Relevance in the entities world) for the page, in the first column.
The column “no of pages” shows the number of competing pages that are using this entity. They are sorted automatically by the most used ones (most important entities).
For existing content: we suggest analyzing the table to find out the entities you are missing. Expand and structure your content (using the main entities in the Headers) based on this list.
For new content: we recommend you use the SERP Explorer instead of the Entities GAP Analysis module. As we told you you can play with the number of selected results and the “no of pages” to extract the list of Entities. We suggest not going with less than 3 pages sharing the results to avoid some irrelevant entities popping up.
With Surfer SEO, you have a feature to import your own entities, which makes it very convenient for your writers!
How to Use the About and Mentions Properties for On-Page Optimization
The about property should refer to 1-2 entities at most, and these entities should be present in the H1 title.
Mentions properties should be no more than 3-5, depending on the article’s length. As a general rule of thumb, an entity (or sub-topic) should be explicitly mentioned in the markup schema if a paragraph or a sufficiently significant portion of the document is devoted to the entity or for disambiguation purposes.
In addition, such “mentioned” entities should also be present in the relevant headline, H2, or later.
3. Boost Topic Relevance of Your Backlinks
As a link builder myself, I could not preach this technique enough… This is so ******* good!
As you may know already, Google has stated many times that they were pretty good at detecting good links and ignoring bad links.
Our theory is that Google is using the Google Knowledge Graph to determine the relevance between 2 targets. If both targets have a match in entities, it passes the link juice. If it didn’t, then Google just ignore it.
Another way to put this is that the source and target page need to be in the same Topical category, and the Pro version of the Entities Swiss Knife will include this analysis, based on the Google NLP algorithm, both on a page and domain level: the best way to qualify your backlinks and check new opportunities.
We have preliminary data to back our theory and we will share them soon, but for now, what we can tell you is that… It is working really well!
Since we are using our top entities in guest post titles and anchor texts, we have seen growth as we have never seen in my last years as SEOs. Here is just one example from many:
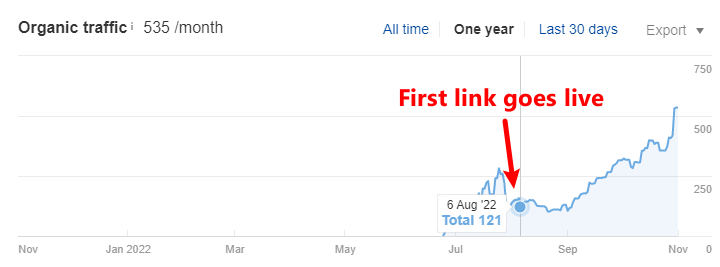
The ranking of the page increased by 340% with just 4 guest post links (2 links per month).
As you see, this is extremely effective! This process is quite simple: just scan your content for its entities, using the “URL Analysis” in our tool, and then, take the 4-5 most relevant entities, and inject them in your guest post titles!
95% of webmasters will leave the slug (URL) as it is (based on the article title), so you will end up having the important entity in the backlink URL and your title, the two most important placements.
The only downside is that, as most link sellers are not offering the option to choose your own titles, you will need to handle the outreach yourself and provide your own articles to the webmasters.
But don’t worry… You’re lucky because my agency is offering this option, for free 😉
of the Industry (No Joke!)
Traffic Authority & Entity Booster
4. Inject Entities in Your Internal Link Anchors to Boost Topical Relevance Between Your Pages
That isn’t a surprise… if injecting entities in external links is a powerful strategy, it is also for internal links!
The process is quite similar to the one for backlinks, you scan your content using the Entities Checker tool and gather a list of your most important entities, then make sure to include them in the anchor texts of your internal links.
Entity SEO implementation: some results
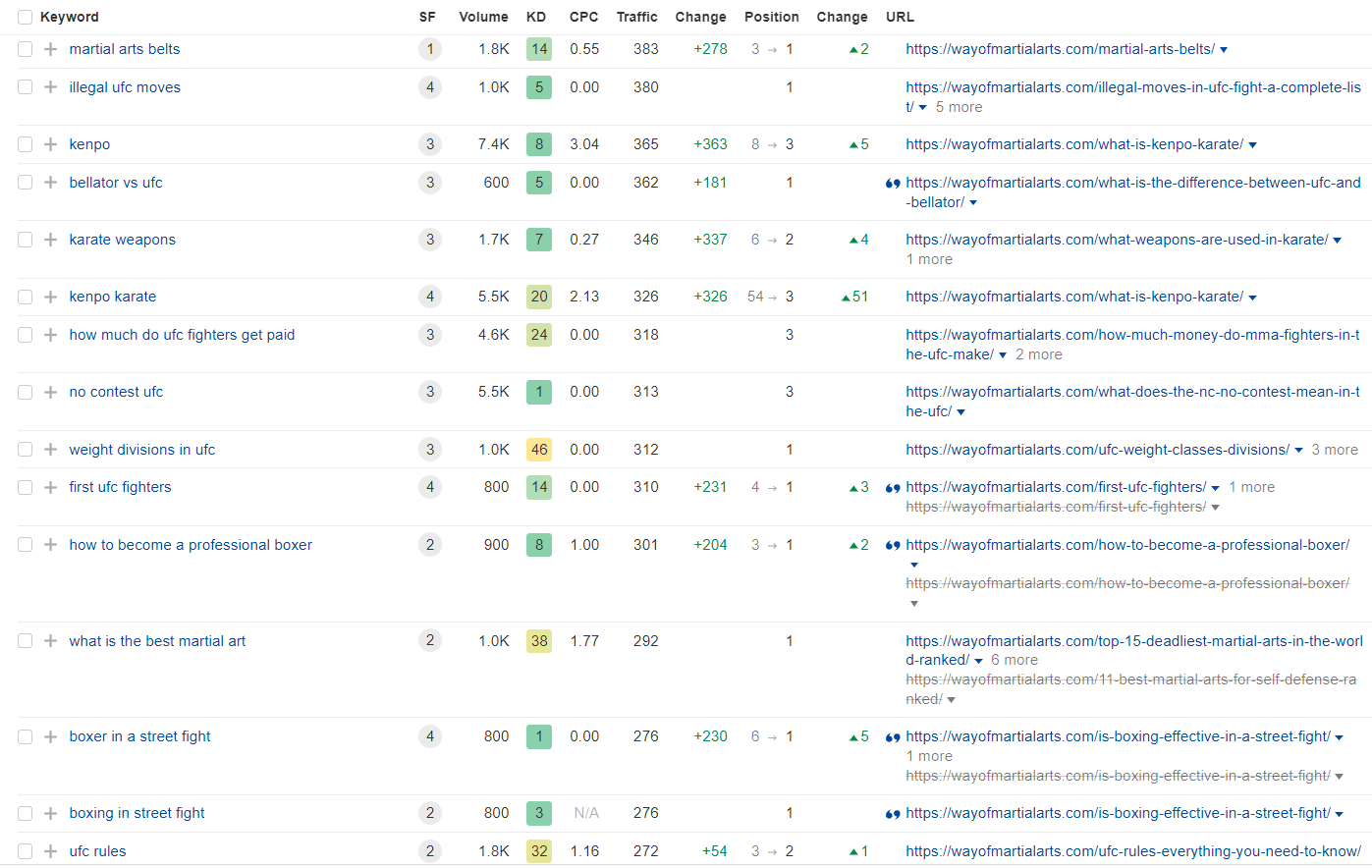
Take a look at this website I’m working on (Max is writing here). This Ahrefs report shows a confrontation of some ranked keywords between October and August when Entities were injected in the structured data at a category level (using the same about property in all the articles of each category).
And look here what happened to Discover after injecting entities in the Organization and Person (for the authors) schema as knowsAbout properties:
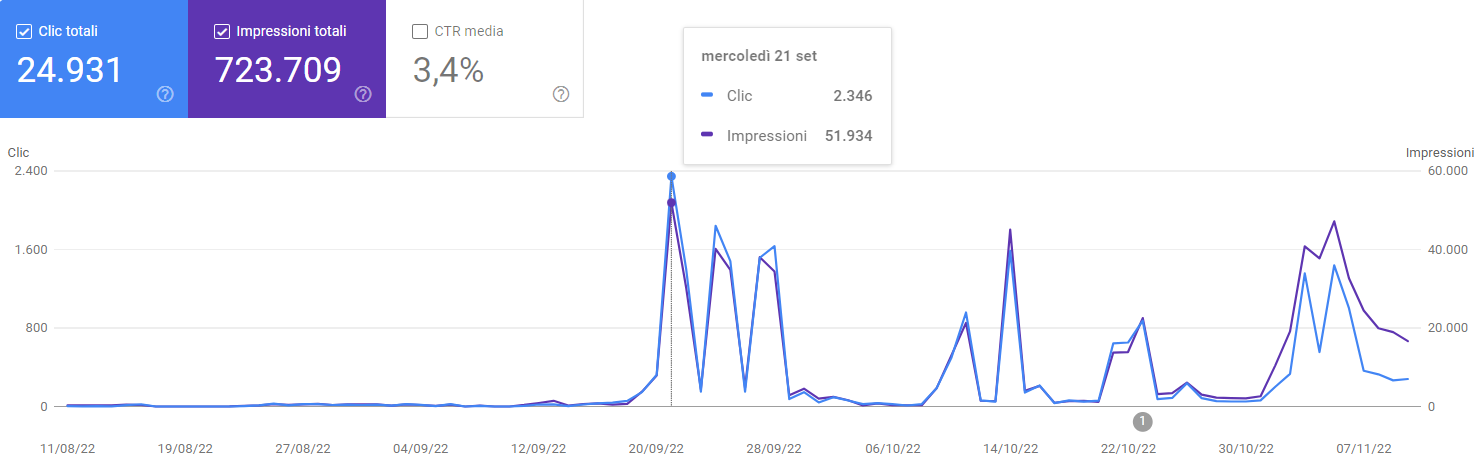
After the September Google Helpful content update, the site gained the authority to be shown in Discover, even for articles that have been there for many months.
Conclusion
2019, when Google integrated BERT into its core algorithm, it’s where everything started.
In 2012, Google started to build the Google Knowledge Graph, a database of 5+ billion entities (Data from 2020), but it’s only recently (in 2019) that Google switched from using keywords to entities, for its ranking algorithm.
Now when Google crawls your content, what it sees is a list of entities, not keywords anymore.
From its database of 5++ billion entities, and 500+ billion facts associated with them, Google connects every piece of content to a list of entities (topics). It’s how Google knows if page X is relevant to topic Y.
If you use entities and your trustworthiness (i.e. Topical Authority) in Google’s eyes is high your site can become a source for those billions of facts associated with an entity.
Using entities everywhere (content, schema, internal & external links) just helps Google to understand your content better (which also helps to rank better). Injecting your entities everywhere just creates a clear map for Google.
If Google has the choice between 2 pages, it will opt for the one that it knows is the most relevant to the topic. Google wants the best for its users… If Google has a doubt about your content relevancy, it will rank another article, just to make sure it fulfills the user intent.
It is now easier than ever (with the right tool!) to optimize for entities and if you are serious about SEO, you should definitely start implementing them in your SEO strategy!
My only regret has been not starting earlier!
This article has been co-authored by me and Max Geraci. The tool The Entities Swiss Knife has also been co-developed by me and Max.
I recommend highly subscribing to my Youtube channel to see the upcoming videos on entity optimization.
Bonus: SEO Entities Checker: A Free Tool With Superpower